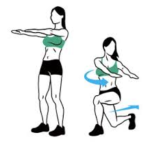
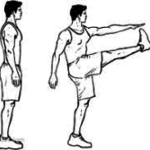
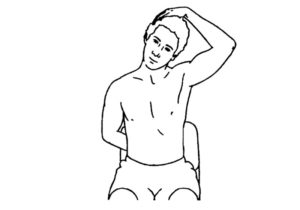
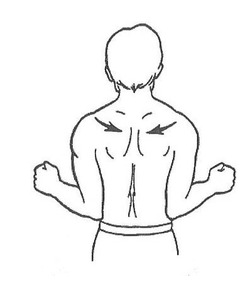
Vestibular disorders are characterized by various types of dizziness such as feeling lightheaded, spinning, floating, tilting, whirling, and feelings of unsteadiness. These episodes of dizziness can last for seconds to hours and may be associated with changing positions, laying down, or can even occur while you are sitting still.
Feelings of dizziness can be very worrisome and it is important to see your physician to investigate more serious causes of dizziness such as a brain or heart condition. However, many causes of dizziness are less serious and are associated with a mechanical problem with your inner ear.
In these cases, a physical therapist at Harbor Physical Therapy can help diagnose these conditions and design an individualized program to help alleviate symptoms of dizziness. Patients with diagnoses such as vertigo, benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), migraines, imbalance, dizziness, and many others may benefit from physical therapy to assist in decreasing feelings of dizziness and improve balance so individuals are able to return to their daily activities.